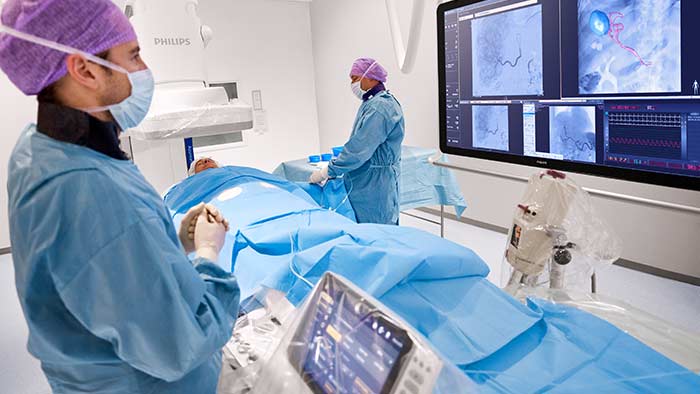
In every successful intervention, critical insight and careful orchestration between imaging, treatment planning, and live guidance play a vital role. You must be able to spot all tumors including those on the periphery of the organ, easily access them, deliver targeted embolisation/ablation, and finally, determine procedural success in the shortest time possible. Philips offers an integrated set of technologies designed explicitly to support you during your interventional oncology procedures. We aim to remove the barriers to efficient and reproducible treatment through step-by-step guidance, full table side control and groundbreaking visualisation techniques. Our portfolio supports consistency and precision which leads to superior care and confident performance.
What is the Philips Onco suite?
Philips Onco suite is a combination of our latest image-guided therapy solution, the Azurion platform with its interventional solutions, workflow options, education, and services. It provides a comprehensive solution for planning and guidance of embolisation as well as biopsy and ablation procedures.
Key benefits
Resources
Experiences using Philips Azurion at St. Antonius Hospital, Nieuwegein, The Netherlands
Introducing the new generation of Philips Azurion
Philips Azurion 7 C20 with FlexArm
Explore the various procedures in interventional oncology suite
-
![Tumor embolisation]()
Tumor embolisation
Solutions for effective guidance in treatment and decision making for tumor embolisation offered by Philips image-guided therapy.
Learn more -
![Tumor biopsy and ablation]()
Tumor biopsy and ablation
Solutions for tumor biopsies and ablations procedures offered by Philips image-guided therapy.
Learn more
Aiming for zero downtime? Uninterrupted workflow? Continuous operational improvement? Partner with Philips as a service provider.
We can take care of the operational management of your medical devices, through predictive maintenance and proactive machine monitoring, whilst you take care of your patients.