Clinical informatics
Bring clarity to prostate cancer diagnosis
Transforming complex procedures into confident care
Demonstrated results in prostate cancer diagnosis
+30%
improvement in high-risk prostate cancer diagnosis using fusion
biopsy vs standard biopsy4
-13.3%
reduction in pathological upgrading to clinically significant prostate cancer with targeted and systematic biopsies vs systematic biopsies alone5
+10%
increase in prostate cancers identified with combined targeted and systematic biopsy compared to systematic biopsy alone5
Featured solutions for prostate cancer diagnosis

DynaCAD Prostate
High-quality fusion guided procedures start in radiology, and DynaCAD offers advanced visualization tools for real-time analysis, review and reporting of multi-parametric MR studies

DynaCAD Urology
DynaCAD Urology provides urologists with an easy way to store, review and manage comprehensive diagnostic and therapeutic data. Create time and workflow efficiencies in your prostate cancer care program.
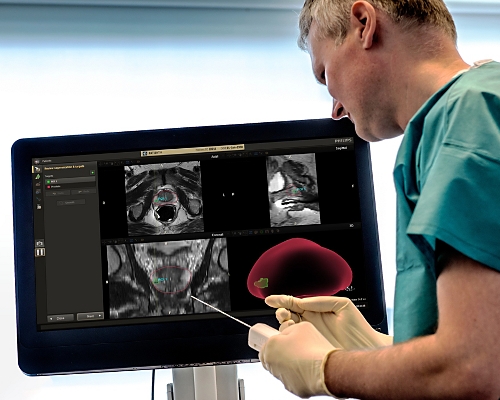
UroNav
UroNav is designed to support you with image guidance during prostate biopsies and focal therapy procedures. It fuses diagnostic MR images of the prostate with live ultrasound images for guided procedures in real time.

Digital pathology
Join the transformation to digital pathology
Our clinical solutions can enhance detection and improve the patient experience by reducing unnecessary biopsies and potentially reducing post-procedure complications. Digital pathology saves time and resources through streamlined collaborative features and case management tools.
“The combination of MRI and ultrasound fusion biopsy is extremely powerful. This technology is too good to ignore.”
Dr. Edward Steiner
Chair of Wellspan Imaging and Radiation Oncology
Wellspan Health, York, PA, USA
Footnotes
[1] Choi YH, et al. Comparison of cancer detection rates between TRUS-guided biopsy and MRI-targeted biopsy according to PSA level in biopsy-naive patients: a propensity score matching analysis. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2019 Feb;17(1):e19-e25. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2018.09.007. Epub 2018 Sep 13. PMID: 30415878.
[2] U.S. News and World Report: 2017 Best Hospitals Ranking (Cancer)
[3] Yarlagadda VK, et al. MRI/US fusion-guided prostate biopsy allows for equivalent cancer detection with significantly fewer needle cores in biopsy-naive men. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2018 May-Jun;24(3):115-120. doi: 10.5152/dir.2018.17422. PMID: 29770762; PMCID: PMC5951198.
[4] Siddiqui MM, et al. Comparison of MR/ultrasound fusion–guided biopsy with ultrasound-guided biopsy for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. JAMA. 2015;313(4):390-397.
[5] Ahdoot M, et al. MRI-targeted, systematic, and combined biopsy for prostate cancer diagnosis. NEMJ. 2020382:917–928. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910038
Disclaimer
Results from case studies are not predictive of results in other cases. Results in other cases may vary.





