20+
Peer-reviewed scientific publications and abstracts
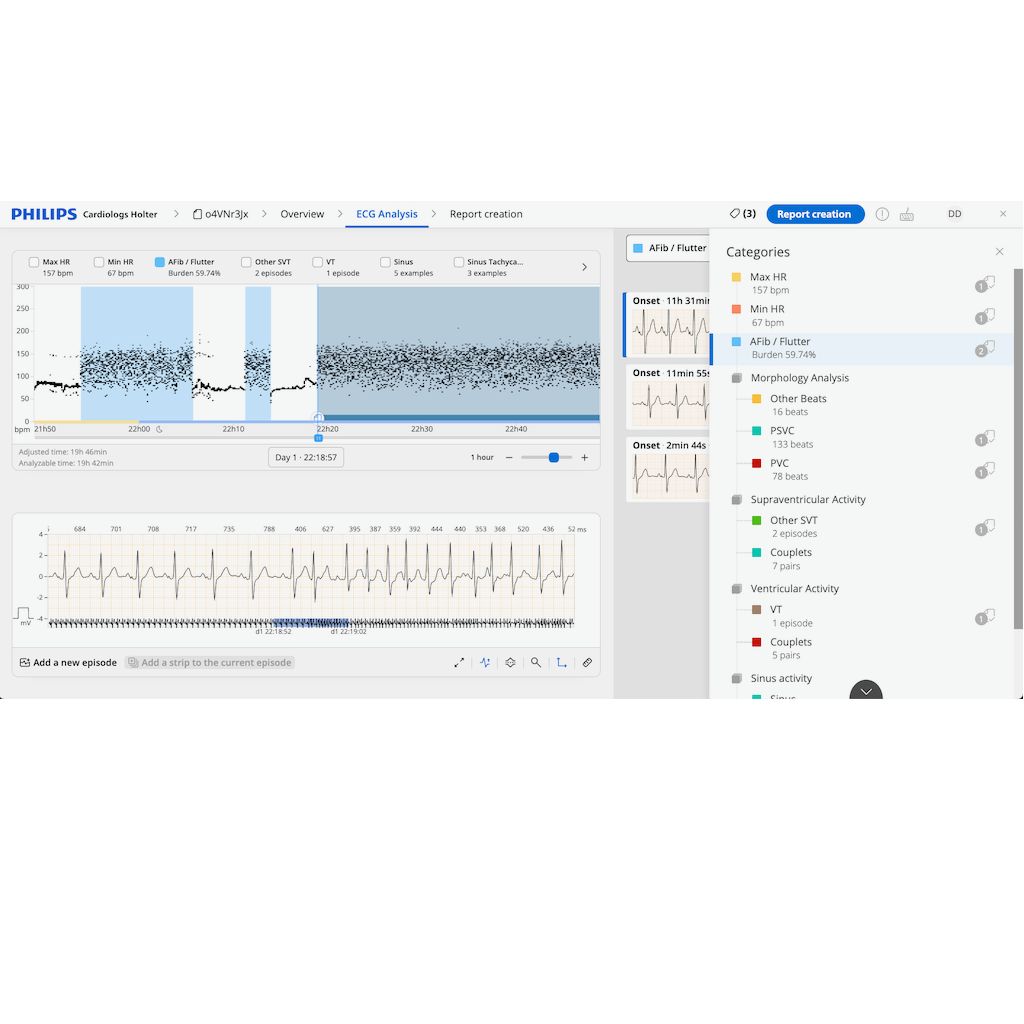
The AI algorithms used in our products have been clinically validated and we continue to innovate.
42%
Reduction in Holter analysis time [2,3]
Based on a clinical study that compared Cardiologs AI solution with a traditional solution [3].