Reading time: 7 Min
Preserving vitamins when cooking: A guide to the healthiest way to cook vegetables
Vegetables can be our best friend when it comes to eating healthily, but do you know the best way to cook vegetables without losing nutrients? After all, what good is it including all those nutritious vegetables, if all their vitamins are drowned in water or fat while they’re being cooked?
Just because there can be a slight vitamin loss by heating, doesn’t mean you have to switch completely to raw food, however. You’ll be pleased to know there are simple ways to cook vegetables properly whilst preserving the all-important nutrients. Read on to discover the effect of heat on vitamins as well as simple steps for the most nutritious way to cook vegetables.
How to preserve nutrients while cooking: Should you have your veggies raw or cooked?
Heat-sensitive vitamins Heat-resistant vitamins
First of all, let’s clarify something. Generally speaking, when cooking vegetables, vitamins are not destroyed – but the nutritional value may be diminished, depending on the way you decide to cook them. The healthiest way to cook vegetables can depend on a number of factors, including the variety of vegetable, how you’re planning to store them and the type of vitamins they contain. For some vegetables, cooking may even help to release vitamins - this is true for carrots and courgettes.
The effects of cooking on vitamins differs. Whilst some vegetable could be more nutritious when cooked, there are types of vegetables whose vitamins may decrease during cooking or heating. This is because some vitamins are heat-sensitive, whilst others are heat-resistant. Here’s a quick and easy guide to each type of vitamin.
A list of heat-sensitive vitamins and foods that contain them includes:
In contrast, heat-resistant vitamins do not get lost when cooked or heated. These include:

How to cook vegetables without losing nutrients: The best time and method
Now you understand about the effect of heat on vitamins and minerals, you’re probably wondering what the best way to cook vegetables without losing nutrients actually is. Unfortunately, there isn’t one answer on how to preserve the nutritional composition of foods, as all foods react slightly differently to heat. The fact of the matter is, it’s all about knowing when to cook and how to cook them. Fun fact: In its raw state, broccoli contains about 540 mg of vitamin C. After cooking it for a few minutes, it reduces to about 260 mg. The longer you cook it, the less vitamin it has. For veggies with heat-sensitive vitamins this is key to remember.
When it comes to cooking vegetables, there are some general rules to keep in mind.
What you need
-
Premium
Airfryer XXL - 6 portions
HD9650/99
- Digital touchscreen
- Rapid Air technology
- black, 1.4 kg
-
- Rapid Air technology
- 1.2 kg, 6.2 L capacity
- Black design
- Connected to our app
- Automatic shut-off
-
- Rapid Air technology
- 4.1 L capacity
- Essential compact Airfryer
- Dishwasher safe
- QuickClean feature
What is the most nutritious way to cook vegetables?
Microwaving, air frying or steaming are amongst the methods proven to preserve the vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients in food. What’s more, the sensitivity of the vitamins during cooking may be accompanied by different solubilities.
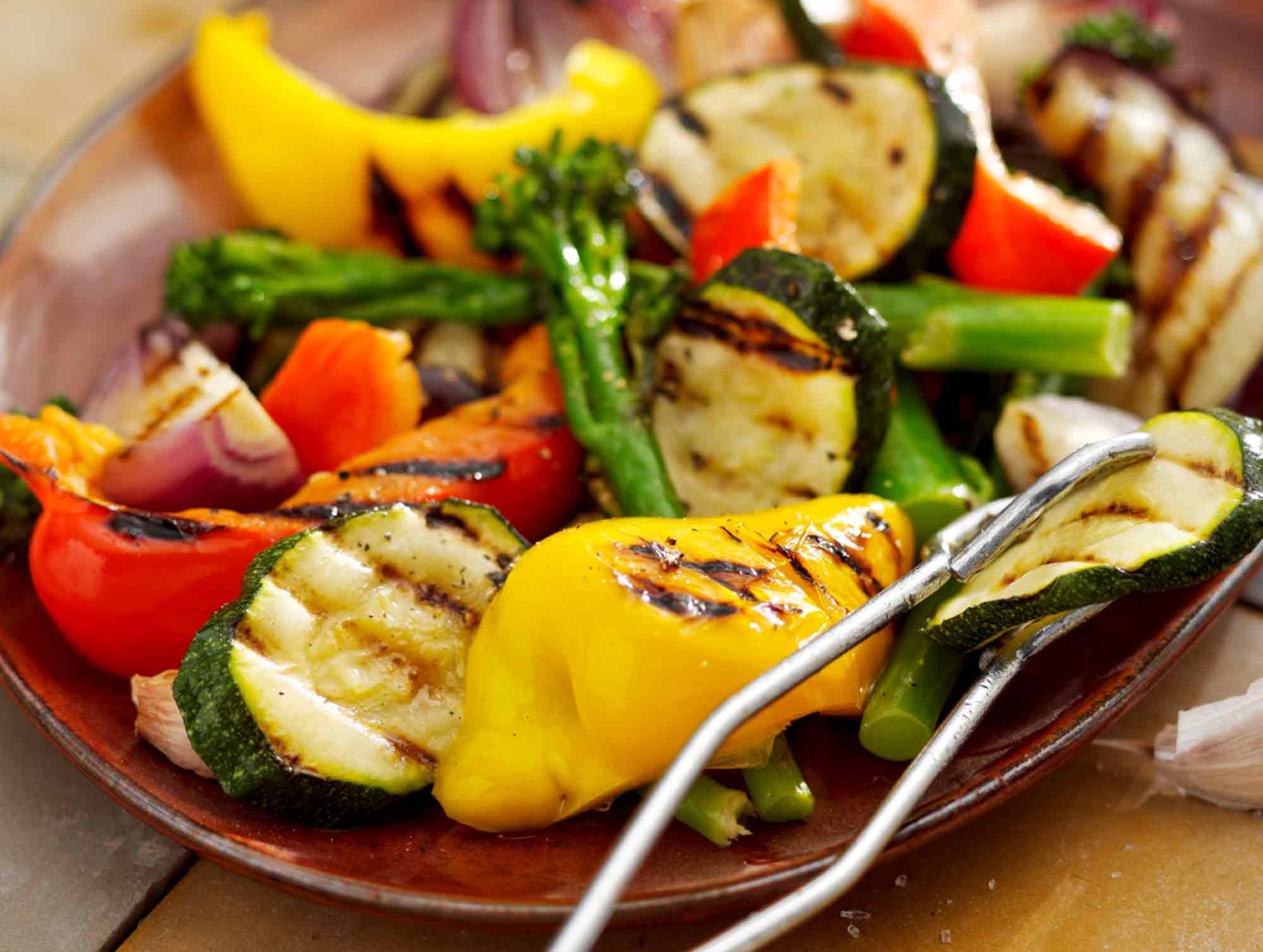
How to preserve nutrients while cooking: Steaming
When steaming, the food is evenly heated by hot steam from all sides and should remain crisp and aromatic.
How to preserve nutrients while cooking: Cooking with fat
Foods that contain many fat-soluble vitamins should be prepared with some oil or fat, otherwise, the body will not be able to absorb these vitamins. However, as with water solubility, they can dissolve in fat when cooking with fat, so you should keep the amount of fat to a minimum. Fat soluble vitamins include:
How to preserve nutrients while cooking: Cooking without fat
Steaming, stir-frying and air frying are some of the methods that can help you cook your vegetables properly and preserve their nutritional content. With an appliance like the Airfryer Viva XXL, the vegetables are not only heated gently and quickly to preserve heat-sensitive vitamins, but can also be prepared with very little oil to prevent the loss of fat-soluble vitamins, such as A, E, D and K. For example, cook vitamin D-rich shiitake mushrooms in the Airfryer, with just a little oil, instead of frying them in oil in the pan.
So, there you have it. Everything you ever needed to know about the effect of heat on vitamins and minerals, and how to preserve nutrients while cooking all in one place. Don’t forget: store your favourite vegetables properly, keep an eye on the type of vitamins they contain, and choose the right type and duration of preparation. This way you can cook your vegetables properly and even keep foods containing heat-sensitive vitamins as nutritious as possible.